Accessible PowerPoint Presentations
This documentation was created using Microsoft PowerPoint 365 for macOS.
Microsoft PowerPoint includes options for adding accessibility information to slides to support access by individuals with disabilities. This information also ensures that Microsoft PowerPoint files maintain a level of accessibility when converted into other formats (e.g., tagged PDF). Creating accessible PowerPoint presentations can be accomplished by incorporating the following practices into your authoring process.
Structure
The structure of the content can provide an organizational and navigational framework for individuals to understand the informational hierarchy and relationship between different sections of content. These structural elements can help determine the organization and logical reading order of the presentation for an individual using assistive technologies.
Slide Title
The Slide Title is used to provide a heading for the slide's content. Slide titles should be unique and descriptive to help users navigate to specific content on the slides. To view and edit slide titles quickly:
- Select View.
- Select Outline View.
- Edit the titles accordingly.
If slide titles are the same, provide a numerical reference to differentiate the first slide from subsequent slides. For example, if there are two consecutive slides that cover the same topic, "How do you use a webpage?", consider adding a number or unique identifier to the end of the title. For example, two titles with the same name could be identified as: “How do you use a webpage? Part 1” and “How do you use a webpage? Part 2”.
Slide Layout
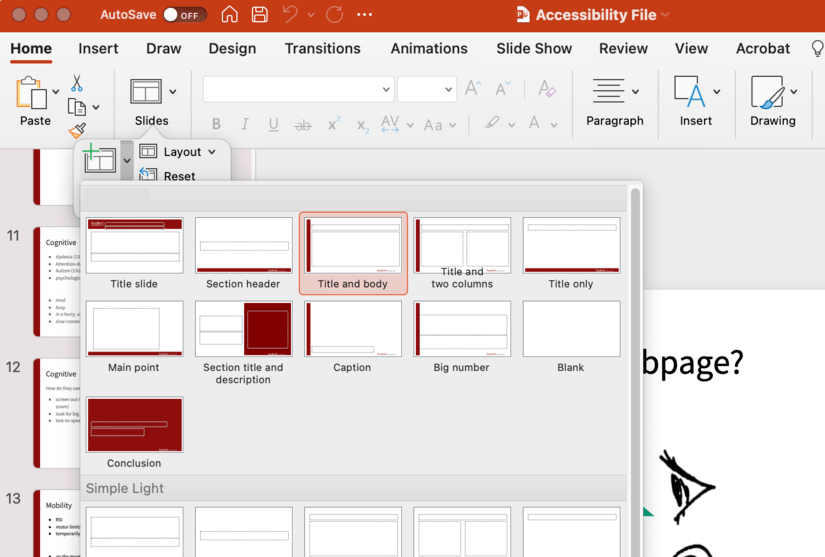
Using preset slide layouts will automatically control the reading order and structure of content placed on the slide. To choose a slide layout:
- To locate Slide Layout, select Home > select New Slide.
- Choose the slide layout that meets your needs.
For more information, read Microsoft’s support page, Apply a slide layout.
Managing Reading Order
If text boxes are separately created from the preset slide layouts, this information may not be in the correct reading order. If content is manually placed onto a blank slide, you will need to assess and manage the reading order using the Arrange button. To review and fix reading order:
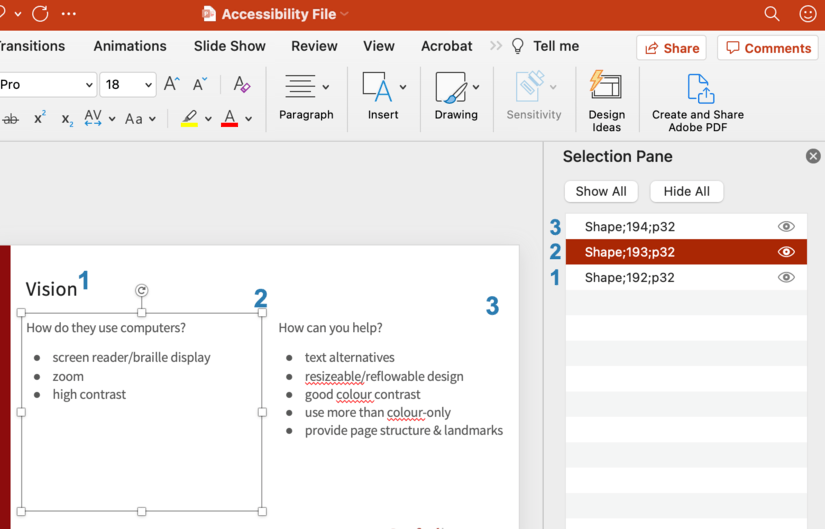
- Select Home > Arrange > Selection Pane
- The reading order begins at the bottom of the list of regions. The first item to be read is at the bottom and the last item to be read is at the top.
- To modify the reading order in the Selection Pane, drag the appropriate item to the proper location in the sequence.
List
Use the built-in list styles to provide users additional guidance. Do the grouped items convey a process or have a logical sequence? If so, then use the number list style. Is this grouped list of items in no particular order? If so, then use the bullet list style.
- Select Home.
- Select either the bullet or number list style.
Images
Images that support the content require a text description (also called "alternate text") to communicate the purpose and/or content of the image. Image descriptions should be short and communicate the main purpose of the image. If a longer description of the image is necessary to fully explain its content, consider alternate strategies outlined on the Images concept page.
To add the alternate text:
- Right-click the image.
- Select Edit Alt Text…
- In the Alt Text window, write a descriptive text.
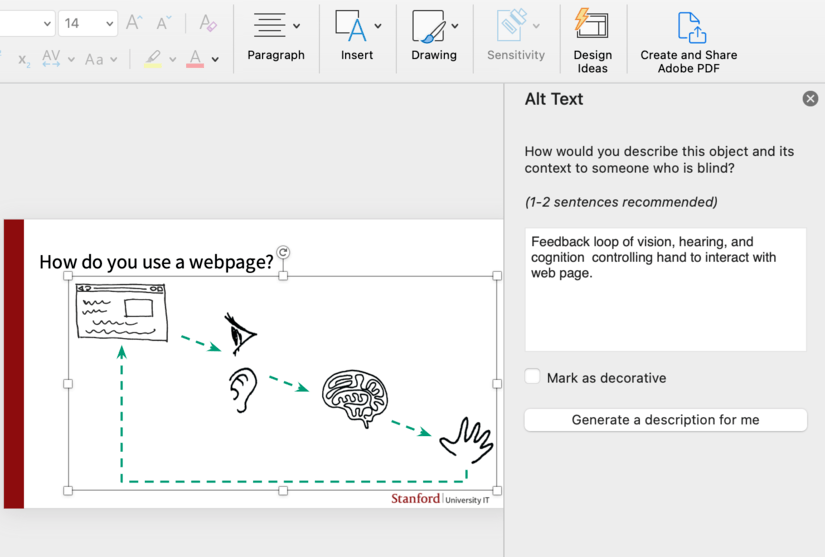
Image description guidelines
For additional guidance on writing effective text descriptions (i.e., alt text), please review theImages concepts page.
- A text description should convey the purpose or content of the image in approximately 120 characters or less.Avoid repeating the same information as contained in the surrounding text.
- For images that are decorative not relevant to the content, use the check box Mark as decorative.
- If the image is complex, consider providing additional information in the surrounding text of the document while providing a shortened text description.
- Do not include the file format in the alt text (Example: .JPEG, .PNG).
- Do not include “picture of” or “image of” in the alt text.
- For older versions of PowerPoint, leave the Title field blank, and only use the Description field for alt text.
Hyperlinks
Documents containing hyperlinks to websites or other online resources can be improved by including hyperlink text that is understood by the reader. For instance, using the full hyperlink URL may not make sense to the reader without some context.
- Highlight the short descriptive phase or words that will become the descriptive hyperlink.
- Select the Link button in the menu.
- In the Address field, add the desired URL.
- Select OK.
For additional guidance, please refer to the Hyperlinks concept page.
If the PowerPoint presentation is intended to also serve as a handout with resource hyperlinks, content authors may want to create a reference slide at the end that lists the full URL of the hyperlink.
Tables
When possible, use a simple table structure for tabular data. Using tables with split cells, merged cells, or nested tables can lead to issues with assistive technologies recognizing the appropriate column and row header information in a data table.
Avoid using a table to manage layout. Instead, use a Slide Layout that orients content into the appropriate visual layout you desire.
Tables should include the following:
- At least one header (the row and/or column).
- Alt Text description summarizing the table.
Specify the header
To mark a header row for a data table:
- Select the table to reveal Table Design. (Note: this tab will only appear if the table is selected.)
- In the far left-hand section, determine the required header type:
- Header row: check the box Header Row.
- Column header: check the box First Column.
Color
Color can be an effective way to communicate ideas and draw attention to information. Insufficient color and contrast can limit the ability of others to perceive and understand the presentation.
PowerPoint offers a variety of slide themes, but not all of these will provide sufficient contrast. To edit Slide Theme colors:
- Select Design > Expand the Color Palette Menu to reveal available color combinations.
- Select Colors to review the pre-built color palettes or select Customize Colors to create slides that have appropriate color contrast.
Select one with accessible contrast, or select Customize Colors to manually select the colors. Alternatively, you can use other methods in Microsoft PowerPoint to remove or change the current theme in your presentation.
For additional guidance, please refer to the Colors concept page.
Exporting to other formats
Do not use the "Print" to PDF option. This will create a PDF document that lacks PDF tags with no heading information, no alternative text, and no logical document structure. These types of PDF documents will create barriers when accessing the document with assistive technologies.
Creating a PDF
Using “Save As” on a Mac
Users of PowerPoint 365 for Mac can export an accessible, tagged PDF. Older versions of PowerPoint may not support this feature.
- Select File > Save As.
- Select PDF
- Choose Best for electronic distribution and accessibility
- Select Save
Using “Save As” on a Windows PC
- Select File > Save As.
- Select PDF > More options.
- In the Save As dialog, select Options.
- Verify in the Options dialog that Document structure tags for accessibility is selected. Select OK.
Creating a PDF with Acrobat
- Use the Acrobat plug-in in the ribbon. Select the Acrobat tab.
- Select Create PDF.