Hyperlinks
Using descriptive text for hyperlinks helps website visitors scan for relevant information, identify outside resources, and choose which links are the most relevant for their needs.
In addition, some assistive technologies, such as screen readers for blind and visually-impaired individuals, have the ability to scan and present a list of all the hyperlinks available on a webpage. This allows a person to quickly jump to the relevant link instead of being forced to listen to the entire page line-by-line.
Tips for hyperlinks
- Communicate the purpose or function of the hyperlink as part of the link name.
- Be as descriptive as possible without being overly long as some assistive technologies (e.g., screen-readers) will read the entire link text before moving to the next text content. Try keeping the hyperlink text under 120 characters.
- Integrate the link into your sentence, sighted users will see the link, and screen readers will hear the link.
- Ask yourself when writing a link text, "Will the reader know where they are going just by the link text alone?"
Assistive Technology and Hyperlinks
Some assistive technologies can extract all the hyperlinks on a web page and present that information to the user. This allows an individual to quickly scan the hyperlinks and jump to the most relevant hyperlink on the page.
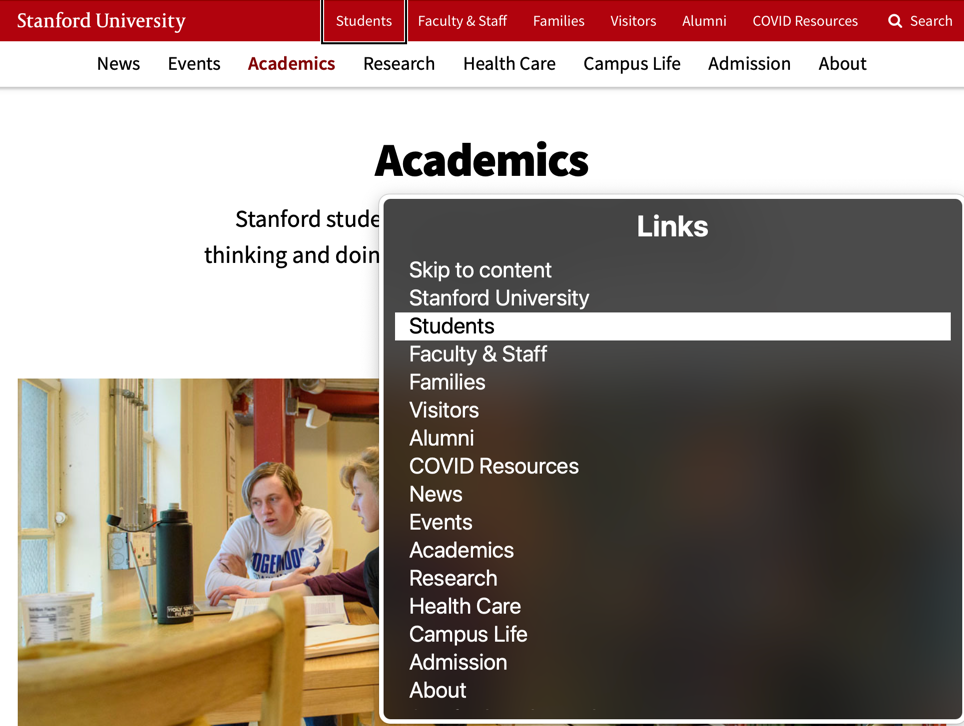
The above example shows how a screen-reader could present the list of hyperlinks from the Stanford website. Providing descriptive link text can simplify interacting with electronic content and provide greater opportunity for the website visitor to find and engage with the information they are seeking.
Examples of appropriate link text
- Read about the basics of vaccines at the CDC.
- Be sure to read about the Stanford Honor Code.
- Read the following: Alt Text Decision Tree and The Definitive Guide to the Alt Text Field.
- Learn more about color accessibility for evaluating contrast and understanding WCAG 2 color requirements.
Examples of inappropriate link text
- Click here to read the CDC article.
- Read our honor code policy: More Info
- Read about alt text in Article 1 (Read More) and Article 2 (Read More)
- Learn more about color and accessibility here and here.
Image Links
When using an image as a link, there are some specific rules that need to be followed. As discussed on the image ALT text concept pages, using an empty ALT text is fine for images that are purely decorative. However, as soon as you put an image inside of an anchor (link), then that image is no longer decorative, it is functional and the ALT text of the image needs to follow the function and not be descriptive of the actual image. For example:
<a href="https://stanford.edu"> <img src="image.jpg" alt="Stanford University Homepage"> </a>
There are some variations on this pattern though that should be addressed. If there is link text in addition to the image, then having an empty ALT text is preferred.
<a href="https://stanford.edu"> <img src="image.jpg" alt="">Stanford University </a>
If the image link is redundant to another link that is adjacent to the image link, then removing that first link entirely from assistive technology is preferred. This involves two steps. First, remove the image link from the tab order using a negative tabindex value. Second, add an aria-hidden attribute to the image link (adding a role of presentation to the link would also work). In this case though, we need to add the ALT text back in for cases where a user might be using both a screen reader and a mouse (low vision users).
<a href="https://stanford.edu" tabindex="-1" aria-hidden="true"> <img src="image.jpg" alt="Stanford University"> </a> [... snip ...] <a href="https://stanford.edu"> Stanford University </a>
