WebAuth with a Macintosh
WebAuth is being deprecated and will be retired soon.
To get help transitioning from WebAuth to SAML, visit SAML (Authentication) or the WebAuth Announcement page.
Overview
To WebAuth your web pages with a Macintosh you must first mount your WWW folder using Stanford OpenAFS and then set the appropriate permissions in your WWW folder. You then create a .htaccess file using TextEdit and place this .htaccess file into your WWW directory using a file transfer program such as Fetch.. It's actually quite simple. TextEdit comes as part of Mac OS X and Stanford OpenAFS is available free from the OpenAFS at Stanford web site. If you don't have Fetch, you can get it from the Essential Stanford Software site.
Most people use WebAuth on pages contained in subfolders inside their WWW directory. This is because WebAuth actually works on the folder, not the page, so creating a subfolder is almost necessary (unless you want to protect your entire home page.) In the example below we assume you want to protect web pages inside a folder called "classproject" which is located inside your personal WWW directory.
Note: The Workgroup Manager is a web application that allows you to define groups of Stanford community members for use in various online applications (not just a web page or group of pages) that also utilizes web authentication (WebAuth). See the overview for Workgroups and the Workgroup Manager if this is the type of authentication you need.
Setting WebAuth permissions
Put your AFS home folder onto your desktop
- Click and hold the Stanford Desktop Tools icon
 to display a popup menu. Click Mount AFS Volume.
to display a popup menu. Click Mount AFS Volume.
(Alternatively, from your Applications folder click Stanford, click AFS, and double-click AFS Controller.) - When the Mount AFS Volume window opens, under "Mount volume belonging to," click My Home and then click Mount. If you need help doing this, see Using Stanford OpenAFS for Macintosh.
- A window will open on your desktop. Inside this window are your WWW files and folders: you are now in AFS. Double-click the WWW folder to open it.
Set the appropriate permissions
- Hold down the CONTROL key and click-hold the "classproject" folder. A contextual menu for that folder will pop up.
- Slide your cursor down to AFS submenu. Move the cursor to the right to open this submenu:
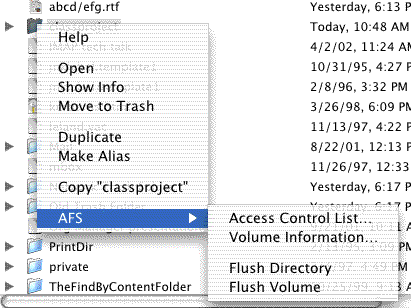
- Select Access Control List .... An Access Control List window will appear.
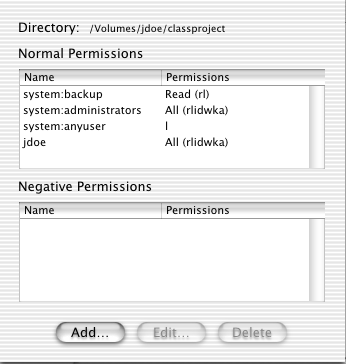
This window shows what permissions are currently controlling the "classproject" folder. Basically, you need to change "system:anyuser l" to "system:anyuser none" (which will cause it to disappear), and add or edit a permission that says "system:www-servers rl" so the web server can protect the files inside this folder.
To get rid of "system:anyuser"
- Click on and highlight "system:anyuser" in the Access Control List window.
- Click the Delete button.
- A Delete Permission box will appear, asking if you're sure about this. Click the Delete button.
- The Access Control List window will refresh to indicate the ACL you deleted is gone.
To add "system:www-servers"
- Click the Add... button. A nameless dialog box will appear.
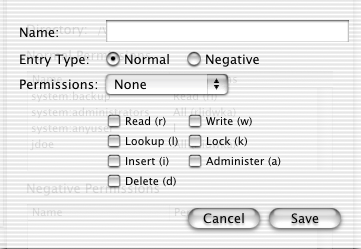
- In the Name: field, type:
system:www-servers
(Don't forget the colon (":"), without any spaces, between the word "system" and the word "www-servers".)
- Click on the Read (r) and Lookup (l) buttons.
- Click the Save button.
To edit "system:www-servers"
If "system:www-servers" is already present in the Access Control List window, it may have ACLs different than the "rl" permissions you need. You'll have to edit them:
- Click on and highlight "system:www-servers" in the Access Control List window.
- Click the Edit... button. A nameless dialog box will appear.

- Click on the Read (r) and Lookup (l) buttons.
- Click the Save button.
When you're done making these changes close the Access Control List window.
Creating a .htaccess file
Open TextEdit
- Double click the TextEdit icon. (It's in the Applications folder.)
- Close the window called "Untitled.txt".
- Go to the TextEdit menu and select Preferences ... .
- Click the Plain text button in the New Document panel of the Preferences dialog box.
- Close the Preferences dialog box.
- Go to the File menu and click New.
Type the WebAuth instructions you want to use
- In the new TextEdit window upon your screen you can type your two lines of WebAuth instructions. We recommend, however, that you simply cut and paste the WebAuth code you want from our list of common ready-made WebAuth directives. This list tells you which WebAuth instructions to use for which WebAuth purpose.
If you do cut and paste from the list, your next step would be to edit the file. For example, if you copied and pasted this code from the WebAuth list:
- AuthType WebAuth
- require user sunetid1
- AuthType WebAuth
- require user gsmith
- Press RETURN once. The WebAuth instructions in your .htaccess file won't work unless they are followed by at least one carriage return.
Save the TextEdit document
- Go to the File menu.
- Click Save.
- In the Save as field, type htaccess.
- In the Where drop down menu, select Desktop.
- Make sure the Plain Text Encoding field says Western (Mac OS Roman).
- Click Save.
- Close the TextEdit document (which is now titled htaccess).
Putting the .htaccess file into AFS
Note: File names that begin with a dot are reserved for the system and are hidden. You need to use an file transer application, such as Fetch, that will allow your .htaccess file to remain visible.
- Open Fetch by double-clicking its icon..
- It's in the Applications folder (or the Dock if you placed it there).
- If you don't have Fetch, you can get it from the Essential Stanford Software site.
- When the Fetch connection box appears,enter cardinal.stanford.edu in the Host name field. and Connect using: SFTP. If you need help doing this, see the instructions for using Fetch.
- Use your SUNet ID in the Username: field and SUNet ID password in the Password: field.
- Click Connect.
- Navigate to the web folder you want to protect. (In this case, you'd double click on the WWW folder, then double click on the "classproject" folder.)
- Drag your htaccess file into that folder.
Change the name htaccess to .htaccess
- Still in the Fetch window, select (so it's highlighted) the htaccess file you just placed. Its name may have changed to htaccess.txt, but that's okay: it's still the same file.
- Click on the name of the file again so that it highlights.
- Change the name of the file to .htaccess. Don't forget to add the dot (".") in front of the word htaccess!
- Press RETURN.
- Terminate your connection to AFS by clicking the "close" button on the Fetch window.
- Close the application by selecting Quit Fetch under the Fetch menu.
