System requirements
- Windows 8.1 and above, including both 32- and 64-bit platforms
- macOS 10.10 and above
Program execution
- PC: If the computer is running Windows 2000 Service pack 2 or below display an error message and quit.
- Confirm that the user who is logged in has administrator rights.
- The installer may prompt for administrator credentials.
- If the user does not have administrator rights display an error message and quit.
- Log all program activity to the activity log file
- Windows: “C:\ProgramData\Stanford\SNSR\snrt_activity_log.txt"
- macOS: “/Library/Logs/Stanford/SNRT.log"
- Get all of the physical network interface hardware addresses and tag them as "wired" or "wireless."
- Download the latest configuration file from the SNSR server.
- Contact the SNSR server to get the subnet and organizational template options:
- The final completion URL (optional)
- Is BigFix required?
- Is antivirus software required?
- PC: Download the latest Microsoft Malicious Software Removal Tool.
- Skip if the most recent MSRT has already been run
- See if it is safe to check for weak administrator passwords. Disable password strength-checking if:
- an account lockout threshold has been assigned
- an alternative authentication method (e.g., biometric) is in use
- Mac: FileVault is enabled
- Get the local computer name.
- Get the user's SUnetID (if they are authenticated to the Stanford MIT Kerberos realm).
- Get the user's login name.
- Get the operating system version.
- Get the computer Make, Model and Type.
- Get the name and version of the user's virus protection program (if a recognized program is installed).
- PC: Information is obtained from the Windows Security Center if possible
- Mac: Only Stanford's site-licensed Sophos AV software is detected
- See if the user is missing any important patches.
- PC: critical patches as defined by Windows Update
- Mac: “recommended” macOS and security updates as defined by Software Update
- Exclude any patches specified in patch_exclusions.txt on the SNSR server
- If it is safe to do so, get the names and passwords of all administrator accounts that have been assigned empty passwords.
- If weak passwords are found, display them to the user (but do not log them), and require that they be changed
- See if BigFix has been installed.
- PC: Set the DHCP Broadcast Flag to false in discover packets on Vista.
- Estimate actual network throughput .
- For slow links, warn users if OS patching is likely to take more than 15 minutes.
- PC: Run the Microsoft Malicious Software Removal Tool in quiet mode
- If a worm or virus was found and removed, log the fact
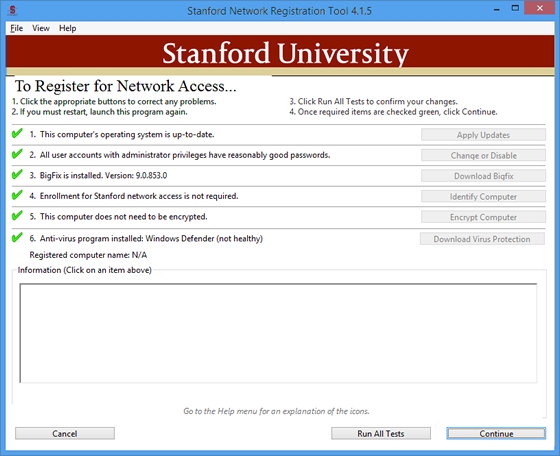
- Alter the UI to reflect the status of:
- virus protection
- OS security patches
- administrator passwords
- BigFix
- Device Enrollment
- Disk Encryption
- Display the computer's newly assigned DNS host name.
Command button actions
Virus Protection Download button
Open the default browser and navigate to the appropriate web page for AV downloads. The URL is read from the configuration file.
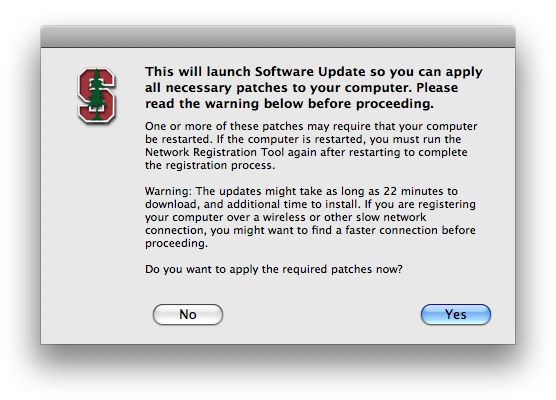
Software Update button
PC: Patching is performed automatically using the Windows Update service.
Mac: Launch the “Software Update” application.
Warn if patch download and installation will likely take more than 15 minutes:
Change Passwords button
Load a window that will allow the user to change weak passwords:

Download BigFix button
Open the default browser and navigate to the appropriate web page. The URL is read from the configuration file.
Cancel button
Ask the user if they really want to exit because the computer will not be registered if they do. If they confirm that they really want to exit, then end the program.
Run Tests Again button
If the user is required to patch the computer before registering, this button will appear. If a reboot is not required, they can click on “Run Tests Again” to check for compliance. If all required patches are found, they will be able to continue with registration.
Continue button
PC: Make the registry changes necessary to security-harden the computer
PC and Mac: Build an HTTP GET URL containing the computer MAC addresses ("MAC") appropriately tagged as "wired" and "wireless," OS version ("OS"), IP Addresses ("IP"), Make of the computer ("MAKE"), Model of the computer ("MODEL"), and Computer Type ("TYPE"), and send it to the server.
Registry changes
Selecting "What Settings Will Be Changed?" from the Help Menu will automatically generate a complete changes document that will be opened in the default browser.
Computer model details
PC
PC model information is obtained by a WMI call that retrieves computer model information provided by the manufacturer.
Mac
Mac model information is obtained by running “sysctl hw.model” from the command line and retrieving the model from the sysctl output. Sysctl gets this string from OpenFirmware and will necessarily change as new models are released. The string that is returned is a representation of the actual Model name. For example, “PowerMac3,6” is a PowerMac G4 and "PowerMac7,2” is a PowerMac G5 See Apple documentation for an up-to-date list of translations.
Computer type details
PC
PC Type information is obtained by a WMI call that will retrieve one of the following:
- “Other” Could use Virtual here for VM machine.
- “Unknown”
- “Desktop”
- “Low Profile Desktop”
- “Pizza Box”
- “Mini Tower”
- “Tower”
- “Portable”
- “Laptop”
- “Notebook”
- “Hand Held”
- “Docking Station”
- “All in One”
- “Sub Notebook”
- “Space-Saving”
- “Lunch Box”
- “Main System Chassis”
- “Expansion Chassis”
- “SubChassis”
- “Bus Expansion Chassis”
- “Peripheral Chassis”
- “Storage Chassis”
- “Rack Mount Chassis”
- “Sealed-Case PC”
Mac
Mac type information is obtained by running “sysctl hw.model” from the command line and parsing the model from the sysctl output (if the model contains the string “book” it is assumed to be a laptop). The Mac type will be either “Desktop” or “Laptop”
SNRT Removal Instructions
macOS (from terminal)
killall SNRTNotifications
rm -R /Library/Application\ Support/Stanford/snrt_service
rm -R /Library/Application\ Support/Stanford/SNSR
rm -R /usr/local/stanford/snsr2019
Windows - A removal tool is available here.
- The SNRTWindowsService Service: %PROGRAMDATA%\Stanford\SNRTWindowsService
- The run reg key value SNRTNotifications needs to be removed: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- The SNRT service reg key should be removed: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Stanford\SNRT_SERVICE
