AI Playground Quick Start Guide
About the AI Playground
The Stanford AI Playground is a user-friendly platform, built on open-source technologies, that allows you to safely try various AI models from vendors like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic in one spot. The AI Playground is being managed by University IT (UIT) as a pilot for most people at Stanford. This includes all active faculty, staff, students, postdocs, visiting scholars, and affiliates.
AI Playground: An Introduction
With this short video, discover how exploring AI tools and technologies can benefit you. Plus, find out how the AI Playground works overall with short demos of how to use prompts and understand replies.
Playground safety

Do not use high-risk data in your attachments or prompts.
And remember, while large language models (LLMs) are advanced tools, they are not flawless and may create errors or hallucinations. Take caution before trusting or using results verbatim.
Dive in and get started with a visit to the AI Playground!
How to log into the Playground:
- Visit aiplayground.stanford.edu
- Follow the steps to log in with Single Sign On (SSO).*
* You might be taken to an Information Release settings page, especially if it's your first time visiting.
- Select your consent duration preference.
- Click Accept to keep going. (All data shown is kept within Stanford systems.)
Note: The Information Release is part of the university's authentication system and is used solely for logging into the platform. This information will not leave university systems and is only shared at the time of logging in. Learn more in the FAQ section under "Data privacy and security in the AI Playground."
How to enter a prompt:
- To use the default settings with your prompts, navigate into the empty field at the bottom of the welcome screen.
- Type a prompt into the field and press the Return or Enter key.
- Once you receive the result, continue to modify or refine your prompt.
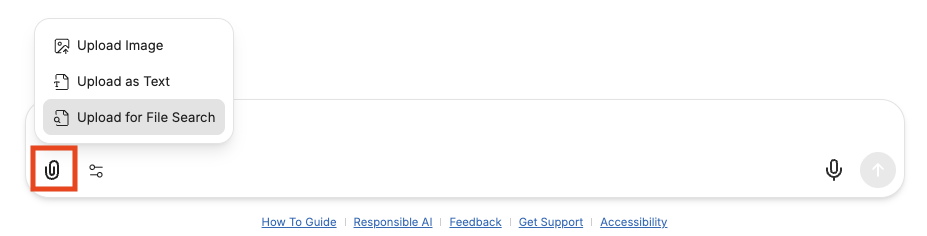
Attach Files from the prompt bar
Several file tools are available from the prompt bar in the Attach Files menu (paperclip icon):
- Upload Image.
- Upload as Text: Makes it easier to pull the content of uploaded documents directly into your conversations. Includes enhanced OCR support using Mistral’s OCR API, so that images and PDFs can be converted to text automatically.
- Upload for File Search: File Search stores the uploaded document in a way that the AI can search and fetch relevant pieces when needed, rather than reading it all at once. This is ideal for large files or when you need to have a lengthy conversation about a file.
Please note, the paperclip icon does not appear when using agents.
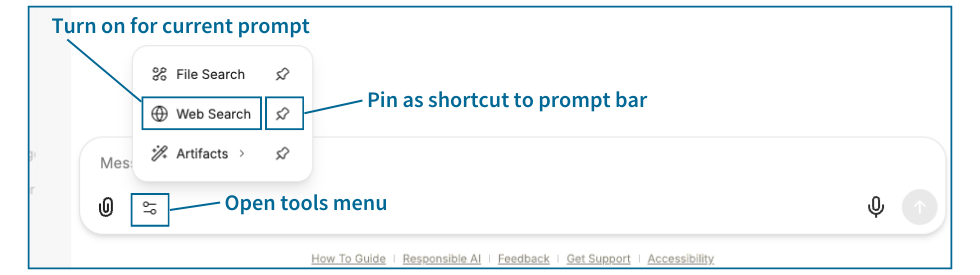
Launch Tools from the prompt bar
Specialized tools are now built into the prompt bar.
To use, open the Tools menu on the prompt bar and select the tool.
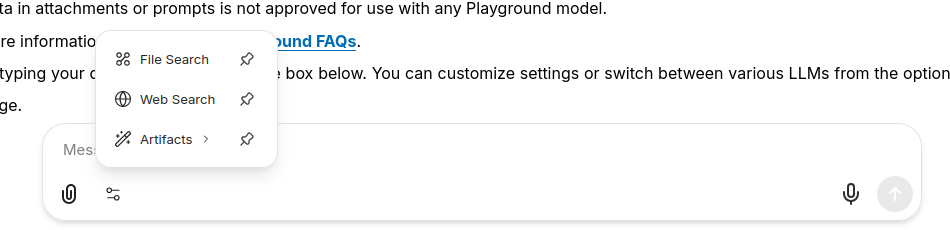
- File Search: When selected, a "File Search" indicator will appear in the prompt bar to show it is active. With the Upload for File Search option (from the Attach Files menu), the File Search tool (from the Tools menu) enables semantic retrieval of data in files in an efficient way. File Search stores the uploaded document in a way that the AI can search and fetch relevant pieces when needed, rather than reading it all at once. This is ideal for large files or when you need to have a lengthy conversation about a file.
- Web Search: When selected, a "Search" indicator will appear in the prompt bar to show it is active. Once you enter your prompt, linked online sources will be included in the response to your prompt.
- Artifacts: When selected, an "Artifacts" indicator will appear in the prompt bar to show it is active. Optionally, choose either "Include shadcn/ui components instructions" or "Custom Prompt Mode" from the Artifact tool's flyout menu. For more on Artifacts, see the Artifacts section of this guide (section 9).
Tip: To add a shortcut for any of these tools to the prompt bar, click the pushpin icon next to tool name in the Tools menu.
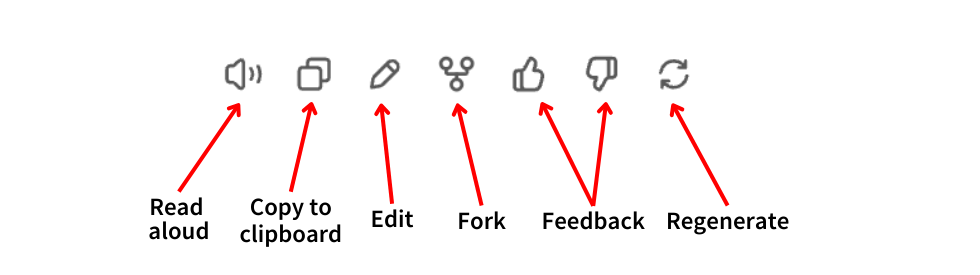
Interact with a message in the conversation
Beneath your prompts and the responses generated by the LLMs, you'll find several more advanced features:
- Read aloud: Read outs the message via a computer-generated voice.
- Copy to clipboard: Copies the content of the selected message to your clipboard to be pasted into another window or program.
- Edit: Allows you to edit your prompts as well as the responses of the various models.
- Save & Submit: Saves your edit and resubmits the information to regerate the AI's response.
- Save: Saves your edit without regenerating the response.
- Cancel: Closes the edit window without saving changes.
- Fork: Creates a new conversation that starts from the specific message selected. This can be useful for refocusing the conversation, creating branching separate scenarios, preserving context, and more.
- Feedback: On any response, choose the thumbs up or thumbs down icon for specific feedback options. Select the best choice.
- Regenerate: Forces the model to try to create a new response without any additional context.
Temporary Chat
Temporary Chats are excluded from your personal search results, cannot be bookmarked, and are automatically deleted after 30 days. You can open the Temporary Chat option at the top right of the main/center panel of the AI Playground. Temporary Chat can be used to keep your chat history clean and focused, and for sensitive topics, quick experiments, or anything you don’t need to permanently save.
Select your preferred model at the top of the page. You can also adjust and switch models in the middle of a conversation.
- For example, you can start a conversation in OpenAI with the prompt "Write an article about topic A" and then switch to the DALL-E-3 agent to request an image to go with the article, then switch to Anthropic and request a list of headline options to go with the article.
Choose between these available versions for each model.
Azure OpenAI (ChatGPT) models
Model Best for Strengths Notes Use if you need gpt-5 Complex reasoning, document processing (text, images, PDFs), long form synthesis, and advanced coding Strongest reasoning and instruction following capabilities, reliable with longer context, high quality writing, and code generation Higher cost and much slower than other GPT models, still benefits from structured prompts and examples Intricate work for technical, policy, research, data analysis, coding, mathematics, and executive summaries gpt-5-mini Quick responses and drafts, chat assistants, lightweight code, and email summarization Quick with and good reasoning, better grounding than previous mini models Trades depth for speed, not ideal for long discussions or large documents Quick answers, note cleanup, triage, batch content generation, chatbots, simple agents, rapid prototyping under tight budgets gpt-4o-mini Speedy responses, lightweight content generation, casual coding support Cost-effective, solid for general tasks Think of it as a faster, trimmed-down gpt-4o with solid performance and less nuance Speed and value over cutting edge intelligence gpt-4o Complex reasoning, image and PDF analysis, advanced code generation Deep comprehension, contextual awareness, handles vision input natively Fast and high-performance across creative and technical domains Advanced problem-solving, file analysis, data visualization, coding, long essays gpt-4.1 Complex reasoning, professional communications, data analysis, and code generation Multimodal capabilities, natural conversation flow, coding and technical support May occasionally generate incorrect or outdated information, needs clear prompts for image generation A smart creative or professional collaborator, help explaining complex topics simply, fast and reliable assistance on code or data tasks o1 Academic use, symbolic math, structured data analysis Especially good at formal reasoning and tough equations Slower than gpt-4o, but built for precision in logical tasks Math derivations, proofs, or rigorous academic writing o3-mini Quick responses to technical questions Optimized for STEM, excels at coding, math equations, and science questions Great utility model for short form technical queries Quick help with formulas, equations, code snippets Google models
Model Best for Strengths Notes Use if you need gemini-2.0-flash-lite-001 Very quick responses, great at back and forths conversations Speed focused, ideal for chatbots and mobile use Sacrifices complexity and subtlety for responsiveness Fast responses and do not require deep reasoning gemini-2.0-flash-001 Quick language translation, friendly emails, and strong technical reasoning Handles idioms, coding, high context tasks Sweet spot for blend of speed + sophistication at lower price Multilingual understanding and real-time support gemini-2.5-pro Complex reasoning, advanced coding, multimodal analysis State-of-the-art performance, massive context window (1 million tokens), adaptive reasoning, rich multimodal input support Heavy compute and latency due to deep thinking, still in beta, susceptible to hallucinations Deep research and document analysis, complex web development, reviewing videos, reading charts Anthropic models
Model Best for Strengths Notes Use if you need claude-3-haiku Fast processing of structured tasks and existing data sets Efficient and great at for form fill tasks with clean outputs Use it for quick instruction following or form based responses Snappy summaries, quick data extraction, JSON handling claude-4-sonnet Everyday coding tasks, writing and document review, reading text and images Efficient and fast, large context support, strong reasoning Can be compared to Gemini-2.5-pro, still prone to hallucinations Coding assistance, analyzing screenshots, documents, and writing claude-4.5-sonet Deep reasoning, long running tasks, and advanced coding workflows Handling complex, multistep projects with consistency Most accurate and detailed model from Anthropic Software development, data analysis, research, and agent orchestration DeepSeek models
DeepSeek Open Thinking feature
The DeepSeek models uniquely offer an "Open Thinking" feature, which allows you to see real-time the criteria and inputs that the model is considering as part of its response. This allows you to improve your prompts and better tailor follow-ups. To enable, go to Settings > Chat > Open Thinking Dropdown by Default.
DeepSeek models
Model Best for Strengths Notes Use if you need deepseek-r1 Coding, technical Q&A, advanced math reasoning Open model which gives you insight into its "thinking" process If you want an open alternative to gpt-4, this is a good pick with verbose results Help with engineering tasks, logic puzzles, or lots of information on a single topic DeepSeek-V3-0324 Code generation, complex reasoning, academic-style Q&A Quality responses across logic heavy and technical domains, excels in benchmark style tasks Stronger performance in math and step by step reasoning than earlier DeepSeek models Reliable model for technical asks, code heavy workflows, or educational content generation Meta models
Model Best for Strengths Notes Use if you need Llama-3.2 Adapting writing style and as well as multilingual tasks and translation Open source and responds well to various types of input Capable of great instructional clarity with fast responses Assistance with writing tasks and multilingual support Llama-4 Open source alternative to more expensive models, especially for writing and multilingual tasks Strong performance in summarization, translation, and context sensitive outputs More capable than Llama 3, with improvements in consistency and language understanding Open source model for writing, creative tasks, and research support across languages
To compare the result of two models simultaneously for the same prompt, use the model compare feature.
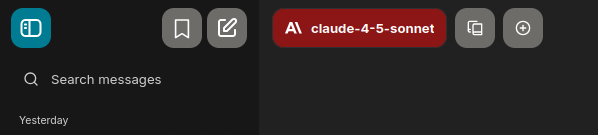
How to compare models side-by-side:
- Select one model for your comparison in the top menu drop-down options.
- Click the plus icon in the top menu options. (See screenshot above.)
- You will notice the selected model is indicated in the prompt field.
- Select the second model for your comparison in the top menu.
- Type and enter your prompt into the prompt field.
- You will see both results side-by-side.
- Once you click out of the conversation, you will be able to see both responses by tabbing back and forth using the numbered tool below the conversation.
The AI Playground also provides access to AI agents and an Azure Assistant, which although they work differently, both provide specific and enhanced functionality.
Note: For direct API access to the models within the AI Playground, developers and tinkerers can use our AI API Gateway service (requires a valid PTA).
Agents
Previously known as plugins, agents are similar to Azure Assistants in their ability to perform tasks like coding, searching documents, or generating images. However, agents offer greater customization and can integrate a larger variety of third party capabilities and model providers.
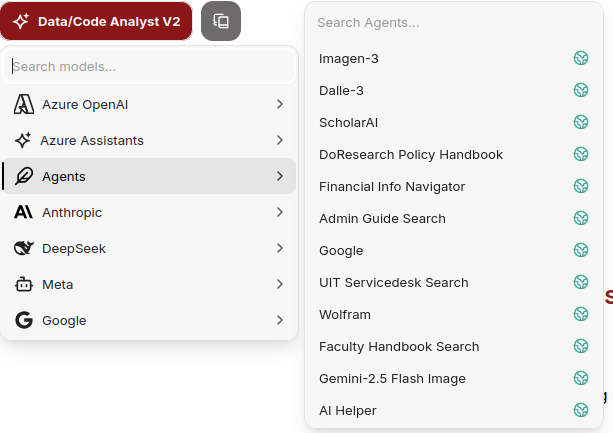
Available agents include:
- Google Gemini 2.5 Flash Image (aka nano-banana): This image generation tool produces images from text prompts. Especially useful for rapid prototyping, brainstorming, or when you need fast image generation without sacrificing overall quality. (Not available to students, postdocs, or visiting scholars at this time.)
- Imagen 3: Generates exceptional photorealistic images based on text descriptions.(Not available to students, postdocs, or visiting scholars at this time.)
- Google: An AI-assisted Google web search. You can use it paired with the GPT models to help conduct Google searches through the lens of an AI agent.
- Financial Info Navigator (FIN): Helps you explore financial questions and transactions. It combines Fingate and the Administrative Guide (both updated weekly) with real-time, read-only access to select Oracle Financials data.
- DoResearch Policy guide: Allows for AI assisted searching of Stanford's comprehensive collection of policies, guidelines, and general information related to the university's research activities.
- Admin Guide Search: Can be used to help answer simple questions about the Stanford Admin Guide through the lens of an AI model.
- Wolfram: Provides computational intelligence for solving complex mathematical equations.
- Faculty Handbook Search: Designed to help you find specific information related to Stanford University faculty policies and guidelines.
- AI Helper agent: Provides quick answers about the AI Playground, showing you how to get more out of the platform. This agent can help identify areas where AI can help support your day-to-day tasks.
Azure Assistants
Azure Assistants function similarly to traditional chatbots but offer enhanced capabilities. Powered by Azure OpenAI, these assistants do not yet support the full range of advanced features available through integration with external tools.
At this time, the only available Azure Assistant is:
Data/Code Analyst
- Best for: Processing files with diverse data and formatting likes spreadsheets and PDFs
- Strengths: Excels at solving challenging code problems and provides more robust data analytics capabilities
- Notes: Power by OpenAI’s code interpreter to help improve data analysis over conventional models
- Use if you need: Assistance reviewing complex spreadsheets and PDFs with unstructured data
Review and manage both saved prompts, files, bookmarks, and more in the right sidebar or panel.
- Open or close the right-side panel using the Open/Close Sidebar button. The button shrinks down when the mouse is not hovering over it, so look for the small button in the middle of the right hand side of the screen.
- Once the panel is open, you can manage the following:
- Prompts: Allows you to save prompts to reuse over and over.
- Memories: Enables remembered context across conversations. Allows all available AI models to recall user preferences, important facts, and context from other conversations (such as details you’ve shared about your role, recurring patterns, or your writing style).
- Parameters: Allows you to fine-tune the model's behavior for specific goals or contexts.
- Attach Files: Allows you to manage files shared with and generated by the models of the AI Playground.
- Bookmarks: Allows you to create and manage bookmarks, which are a new way to group your conversations with the AI models.
- Hide Panel: Collapses right-side panel/sidebar.
Adjust model parameters
You can also use the configuration options button to the right of the selected model to customize your settings.
Before entering your prompt, you can choose to modify the selected model's settings. This is optional, and most people can leverage the default options for the best experience.
Note that the settings might vary slightly for each model type, but many models will have the below configuration options:
- Max context tokens - Defines maximum input size. (1000 tokens is about 750 words)
- Max output tokens - Defines maximum output size. (1000 tokens is about 750 words)
- Temperature - Controls the “creativity" or randomness of the content being generated.
- Top P - Alternative to temperature, refines the number of possible responses based on context provided.
- Reasoning effort - For some models, increasing reasoning effort can help increase quality of responses, by indicating that more computational effort is required. Increased reasoning effort might increase the amount of processing time, as well.
Use bookmarks to organize conversations
Use the Bookmark tool to organize your conversations by similar topics, to find them easily in the future.
Step-by-step:
- When viewing a conversation, click the bookmark icon in the top bar.
- Click New Bookmark.
- Fill in the Bookmark details and click Save.
- To apply the bookmark to the current conversation (likely desired), check the box to “Add to current conversation.”
- Now you can use the Bookmarks selector in the left-side panel to view only conversations with the applied bookmarks.
- Manage, rename, and delete bookmarks in the right-side panel under the Bookmarks section.
You have the ability to share conversations you have had with the models. Your name and any messages you add to the conversation after creating the link stay private.
Share a link to a conversation:
- Click Share.
- Click the Create link button to generate a shareable link.
- Note: Be careful when using this feature. While you must log in to view the link, the conversation will become accessible to any authenticated Stanford users with the link.

Remove a link to a shared conversation:
- Click on your own name in the bottom left corner.
- Click Settings.
- In the new pop up window, click Data controls.
- Next to Shared links, click on the Manage button.
- This will display all the chats with shared links, the date shared, and give you an option to delete the link.
- Note: Deleting a shared link is a permanent action and cannot be undone. Resharing the conversation would include any new information input or generated in the conversation since the original link was generated.

Memories
One way to customize your experience is with the Memories smart system for maintaining context across conversations. This system is on by default, but can be toggled off from the Memories menu in the right-side panel. Memories enable all available AI models to recall user preferences, important facts, and context across your conversations.
Settings
You can also use customize options in the Settings menu that impact your entire AI Playground experience.
To access the settings menu:
- Click on your own name in the bottom left corner.
- Click Settings.

General settings
- Theme: Allows you to change between Light and Dark mode.
- Language
- Render user messages as markdown
- Auto-Scroll to latest message on chat open: When enabled, this will automatically move your view to the last message in the conversation.
- Hide right-most side panel: When enabled, this will remove the pop up side panel menu.
- Archived chats: Allow you to unarchive conversations or delete them from the system entirely.
Chat settings
- Message Font Size: Adjust the size of fonts used in the AI Playground.
- Chat direction: Change the direction of writing systems used in the AI Playground.
- Press Enter to send message: When enabled, pressing the Enter key will send your message.
- Maximize chat space: Increases the visible space used by conversations.
- Open Thinking Dropdowns by Default
- Always show code when using code interpreter
- Parsing LaTeX in messages: When enabled, thinking dropdown menus are expanded automatically. Currently only works with DeepSeek models.
- Save drafts locally: When enabled, texts and attachments you enter in the chat will be saved locally as drafts. Drafts are deleted once the message is sent.
- Scroll to the end button
- Save badges state
- Enable switching Endpoints mid-conversation
- Use default fork option: Defines what information is visible when forking conversations.
- Start fork from target message by default
Beta features
- Toggle Artifacts UI: Show or hide the Artifacts panel to view, manage, or interact with generated outputs like files, code, and designs.
- Include shadcn/ui instructions: Enable guidance and usage tips or examples for integrating or customizing shadcn/ui components directly in your workflow.
- Custom Prompt Mode: Enable to craft and run highly tailored prompts with full control over structure, behavior, and formatting—ideal for advanced or repeatable tasks.
Commands
Turn on these command shortcuts to help streamline prompt configuration and boost productivity.
- Toggle command “@” for switching endpoints, models, presets, etc.
- Toggle command “+” for adding a multi-response setting
- Toggle command “/” for selecting a prompt via keyboard
Data controls
- Import conversations from a JSON file: Allows you to import conversations exported from other GPT chat applications.
- Shared links: Allows you to view and delete all shared conversations under your account.
- Delete TTS cashe storage
- Clear all chats: Deletes all conversations from the left most side panel. (Does not delete archived conversations.)
Account settings
- Display username in messages: When enabled, your name is shown next to your prompts in your conversations. When disabled, prompts you send will be labeled as "You" in conversations.
- Profile picture: Allows you to upload a profile picture for yourself, which is shown in your conversations with the AI models. (Image must be under 2MB.)

Explore the ability to render graphs, charts, webpages, and applications on screen using React, HTML5, three.js, WebGL, and more.
How to enable Artifacts UI:
- To use, open the Tools menu on the prompt bar and select the tool.
- Click on Artifacts.
The button should light up in the prompt bar now to let you know it is enabled.
Note: Artifacts work with each of the major models, but tends to work best with Anthropic and Azure OpenAI models. The artifacts feature does not work in conjunction with agents at this time.
The AI Playground is continually evolving. Features are being updated and added regularly. (View AI Playground release notes.) Here you will find details for using several recently released features.
AI Helper agent
This feature was enabled in September 2025; it can provide quick answers about the AI Playground, show you how to get more out of the platform, and help identify areas where AI can help support your day-to-day tasks. Refer to this article for more details about the AI Helper agent.
Memories
The AI Playground now has a smart Memories system for context across conversations. This allows all available AI models to recall user preferences, important facts, and context from other conversations (such as details you’ve shared about your role, recurring patterns, or your writing style). Refer to this article for more details about Memories
Tools from the prompt bar
These three tools are now available from the new Tools menu built into the prompt bar:

- File Search: With this tool active, you can prompt for semantic retrieval of data in files you have uploaded via Attach Files.
- Web Search: With this tool active, once you enter your prompt, linked online sources will be included in the response to your prompt.
- Artifacts: With this tool active, you can use the improved Artifacts tool for generating code and corresponding prototypes using React, HTML5, three.js, WebGL, and more.
File Search improvements
You can now activate File Search via the prompt bar and keep it active in your chats.
In addition to the new File Search capabilities, the normal attachment feature has also been updated. Now you can upload files as text, making it easier to pull the content of uploaded documents directly into your conversations. This update also adds enhanced OCR support using Mistral’s OCR API, so that images and PDFs can be converted to text automatically.
Feedback on responses
A new chat rating system allows users to provide feedback on AI responses. Your feedback is stored in the conversation metadata, so that conversation is better tailored to you. (Your feedback does not train or fine tune the models in the AI Playground, and ratings do not affect saved user memories.) Refer to this article for more details about Feedback options.
Improved formatting with LaTeX
If you use LaTeX typesetting format for mathematical or technical prompts and responses, you’ll also notice improved formatting of responses that include combined LaTeX typesetting and standard typesetting together.
Add the AI Playground to your phone or computer as a Progressive Web App (PWA)
You can enjoy faster, easier access to the Stanford AI Playground by installing it as a Progressive Web App on your computer or mobile device. UIT has created instructions for Windows, Mac, and iOS.
Please review the Install Stanford AI Playground Like an App page for detailed instructions.
Resources and support
FAQs
Visit our FAQs for more information about using the AI Playground.
AI Playground community
Share and learn from the Stanford community on the AI Playground the #ai-playground Slack channel.
Feedback
Do you have questions, suggestions, or thoughts to share about the AI Playground? Reach out and let us know what's on your mind.